它是干什么的?
$location服务解析地址栏中的URL(基于window.location),让你在应用代码中能获取到。改变地址栏中的URL会反应$location服务中,反之亦然。
$location服务:
- 暴露当前地址栏的URL,这样你就能
- 获取并监听URL。
- 改变URL。
- 当出现以下情况时同步URL
- 改变地址栏
- 点击了后退按钮(或者点击了历史链接)
- 点击了一个链接
- 一系列方法来获取URL对象的具体内容用(protocol, host, port, path, search, hash).
Comparing $location to window.location
| window.location | $location.service | |
| 目的 | 允许对当前浏览器位置的读写 | 同左 |
| API | 暴露一个“裸聊”的能被读写的对象 | 暴露jquery风格的读写器 |
| 是否在AngularJS应用生命周期中和应用整合 | 否 | 可获取到应用声明周期内的每一个阶段,并且和$watch整合 |
| 是否和HTML5 API的无缝整合 | 否 | 是(对低级浏览器优雅降级) |
| 和应用的上下文是否相关 | 否,window.location.path返回”/docroot/actual/path” | 是,$location.path()返回”/actual/path” |
什么时候该用$location
在你想对URL的改变做出响应是,或者在你想改变当前URL时。
它不能用来干什么
在URL改变时,不要刷新整个页面。一定要的话,用低级的API,$window.location.href。
API的总览
$location服务的具体行为取决于它初始化时的配置。默认设置对大多数应用都是适合的,你也可以自定义配置来增加些新特性。
$location服务初始化好以后,你就可以使用jquery风格的读写器和它交互了,你可以获取或者改变当前URL。
$location服务的配置
要配置$location服务,检索$locationProvider并把参数设置成以下这样:
- html5Mode(模式): {boolean}
true – 参阅HTML5模式
false – 参阅Hashbang模式
default: false - hashPrefix(前缀): {string}
Hashbang URLs的前缀 (在Hashbang模式中或者低级浏览器中使用)
default: ‘!’
配置示例
$locationProvider.html5Mode(true).hashPrefix('!');读写器(getter and setter)
$location服务为URL只读部分(absUrl, protocol, host, port)提供读方法,为可读写部分(url, path, search, hash)提供读写方法:
// get the current path
$location.path();
// change the path
$location.path('/newValue')所有的写方法返回同一个$location对象来支持链式风格。比如,要在一条语句中改变URL的多个部分:
$location.path('/newValue').search({key: value});$location服务有一个特殊的replace方法可以用来告诉$lacation服务下一次自动和浏览器同步,上一条浏览记录应该被替换而不是创建一个新的。这在重定向的时候很好用。不这样的话容易使后退按钮失效(点后退时会又触发重定向)。要改变URL而不添加新的历史记录,你可以这样做:
$location.path('/someNewPath');
$location.replace();
// or you can chain these as: $location.path('/someNewPath').replace();注意写方法并不会马上更新window.location,而是在作用域的$digest阶段将多个$location操作合并成一个对windiow.location对象的commit操作。因为多个操作会后对浏览器来说都会只是一个,所以只要调用一次replace()方法就能实现浏览器记录的替换操作。一旦浏览器更新了,$location服务就会将replace方法的标志重置,以后的改变就会创建新的历史记录,知道再次调用replace方法。
写方法和字符编码
你可以给$location服务传递特殊字符,它会根据RFC 3986规则来编码。当你调用写方法时:
- 所有传递给写方法(如path(), search(), hash())的值都会被编码。
- 读方法(path(), search(), hash()不带参数的调用)返回解码后的值。
- 当你调用absUrl()时,会返回各部分经过了编码的完整url。
- 当你调用url()时,返回的值是path, search 和hash,形式是
/path?search=a&b=c#hash。
Hashbang和HTML5模式
$location服务有两种用来控制地址栏URL格式的配置:Hashbang模式(默认)和HTML5模式(使用HTML5历史API)。应用会使用两种模式中相同的API,并且$location服务会使用需要的URL片段和浏览器API来帮助改变URL或者进行历史管理。
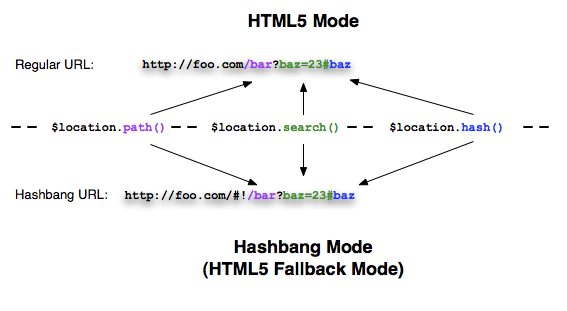
| Hashbang模式 | HTML5模式 | |
| 配置 | 默认 | { html5Mode: true } |
| URL格式 | 所有浏览器都支持hashbang URLs | 在高级浏览器中使用regular URLs,低级浏览器使用hashbang URLs |
| <a href=””> 链接重写 | 否 | 是 |
| 需要服务器端配置 | 否 | 是 |
Hashbang模式(默认mode)
使用这个模式的话,$location会在所有浏览器中使用Hashbang URLs。
示例
it('should show example', inject(
function($locationProvider) {
$locationProvider.html5mode = false;
$locationProvider.hashPrefix = '!';
},
function($location) {
// open http://host.com/base/index.html#!/a
$location.absUrl() == 'http://host.com/base/index.html#!/a'
$location.path() == '/a'
$location.path('/foo')
$location.absUrl() == 'http://host.com/base/index.html#!/foo'
$location.search() == {}
$location.search({a: 'b', c: true});
$location.absUrl() == 'http://host.com/base/index.html#!/foo?a=b&c'
$location.path('/new').search('x=y');
$location.absUrl() == 'http://host.com/base/index.html#!/new?x=y'
}
));支持网络爬虫
你需要添加特别的meta标记在你的文档的头部才能支持对你的AJAX应用的索引。
<meta name="fragment" content="!" />这能让网络爬虫请求带有_escaped_fragment_形式的参数链接,这样你就能识别爬虫并且返回一个HTML的快照了。更多信息请参考 Making AJAX Applications Crawlable。
HTML5模式
在HTML5模式中,$location服务的读写器和浏览器的URL地址通过HTML5历史API交互,这使你能用regular URL path并且搜索各组成部分,和hashbang是等效的。 如果浏览器不支持HTML5 历史API, $location服务会自动回退成使用hashbang URLs。你就不用担心浏览器的支持性了。$location服务总是会用最好的选择。
- 在低级浏览器中使用了regular URL -> 重定向成hashbang URL
- 在现代浏览器中打开了一个hashbang URL -> 重写成regular URL
example
it('should show example', inject(
function($locationProvider) {
$locationProvider.html5mode = true;
$locationProvider.hashPrefix = '!';
},
function($location) {
// in browser with HTML5 history support:
// open http://host.com/#!/a -> rewrite to http://host.com/a
// (replacing the http://host.com/#!/a history record)
$location.path() == '/a'
$location.path('/foo');
$location.absUrl() == 'http://host.com/foo'
$location.search() == {}
$location.search({a: 'b', c: true});
$location.absUrl() == 'http://host.com/foo?a=b&c'
$location.path('/new').search('x=y');
$location.url() == 'new?x=y'
$location.absUrl() == 'http://host.com/new?x=y'
// in browser without html5 history support:
// open http://host.com/new?x=y -> redirect to http://host.com/#!/new?x=y
// (again replacing the http://host.com/new?x=y history item)
$location.path() == '/new'
$location.search() == {x: 'y'}
$location.path('/foo/bar');
$location.path() == '/foo/bar'
$location.url() == '/foo/bar?x=y'
$location.absUrl() == 'http://host.com/#!/foo/bar?x=y'
}
));低级浏览器使用的降级
在支持HTML5 历史 API的浏览器中,$location服务的读写器和浏览器的URL地址通过HTML5历史API交互。 如果浏览器不支持HTML5 历史API, $location服务会自动降级成使用hashbang URLs。你就不用担心浏览器的支持性了。$location服务总是会用最好的选择。
Html链接重写
当你使用历史API模式时,在不同的浏览器中你需要使用不同的链接,但是你需要做的仅仅是指定好regular URL形式的链接,如 <a href="/some?foo=bar">link</a>。
当用户点击这个链接时
- 在低级浏览器中,URL转换成
/index.html#!/some?foo=bar - 在现代浏览器中转换成
/some?foo=bar
如果是下面的这集中形式,连接不会被重写。取而代之的是,浏览器会根据链接重新加载页面。
- 包含target的链接
Example:<a href="/ext/link?a=b" target="_self">link</a> - 指向其他域的绝对路径 Example:
<a href="http://angularjs.org/">link</a> - 当base被定义时,使用’/’开头指向一个不同的base路径。 Example:
<a href="/not-my-base/link">link</a>
服务器端
使用这种模式需要开启服务器端的URL重写功能,基本上你需要重写所有指向你应用的链接(如index.html)。
相对链接
记住要检查所有的相对连接、图片、脚本等。你必须指定你主页面的base url(<base href="/my-base">),或者你使用绝对路径也行,因为相对路径会结合文档的初始绝对路径转换成绝对路径。文档初始路径通常和应用的根路径不一样。
我们强烈推荐应用使用文档根节点开始的历史API,因为它能处理好所有相对路径的问题。
不同浏览器中的链接
因为HTML模式的重写能力,你的用户能在低级浏览器中使用regualr url,在现代浏览器中使用hashbang url。
- 在高级浏览器中会将hashbang URLs冲写成regular URLs。
- 在低级浏览器中使用了regular URL会被重定向成hashbang URL
例子
这里你会看到两个$location实例,都是在Html5模式下,但是在不同浏览器中,这样你就能看出区别了。这两个$location服务是连接在虚拟的浏览器上的。每个input表示了一个浏览器地址栏。
注意,当你输入hashbang url到第一个浏览器的时候(或者反过来),它不会马上重写成regular URL的形式(或者反过来),这个转换只发生在页面加载对初始URL解析的时候。
例子中我们使用<base href="/base/index.html" />
Source
index.html:
<html ng-app>
<head>
<script src="http://code.angularjs.org/angular-1.0.2.min.js"></script>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div ng-non-bindable class="html5-hashbang-example">
<div id="html5-mode" ng-controller="Html5Cntl">
<h4>Browser with History API</h4>
<div ng-address-bar browser="html5"></div><br><br>
$location.protocol() = {{$location.protocol()}}<br>
$location.host() = {{$location.host()}}<br>
$location.port() = {{$location.port()}}<br>
$location.path() = {{$location.path()}}<br>
$location.search() = {{$location.search()}}<br>
$location.hash() = {{$location.hash()}}<br>
<a href="http://www.host.com/base/first?a=b">/base/first?a=b</a> |
<a href="http://www.host.com/base/sec/ond?flag#hash">sec/ond?flag#hash</a> |
<a href="/other-base/another?search">external</a>
</div>
<div id="hashbang-mode" ng-controller="HashbangCntl">
<h4>Browser without History API</h4>
<div ng-address-bar browser="hashbang"></div><br><br>
$location.protocol() = {{$location.protocol()}}<br>
$location.host() = {{$location.host()}}<br>
$location.port() = {{$location.port()}}<br>
$location.path() = {{$location.path()}}<br>
$location.search() = {{$location.search()}}<br>
$location.hash() = {{$location.hash()}}<br>
<a href="http://www.host.com/base/first?a=b">/base/first?a=b</a> |
<a href="http://www.host.com/base/sec/ond?flag#hash">sec/ond?flag#hash</a> |
<a href="/other-base/another?search">external</a>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>script.js:
function FakeBrowser(initUrl, baseHref) {
this.onUrlChange = function(fn) {
this.urlChange = fn;
};
this.url = function() {
return initUrl;
};
this.defer = function(fn, delay) {
setTimeout(function() { fn(); }, delay || 0);
};
this.baseHref = function() {
return baseHref;
};
this.notifyWhenOutstandingRequests = angular.noop;
}
var browsers = {
html5: new FakeBrowser('http://www.host.com/base/path?a=b#h', '/base/index.html'),
hashbang: new FakeBrowser('http://www.host.com/base/index.html#!/path?a=b#h', '/base/index.html')
};
function Html5Cntl($scope, $location) {
$scope.$location = $location;
}
function HashbangCntl($scope, $location) {
$scope.$location = $location;
}
function initEnv(name) {
var root = angular.element(document.getElementById(name + '-mode'));
angular.bootstrap(root, [function($compileProvider, $locationProvider, $provide){
$locationProvider.html5Mode(true).hashPrefix('!');
$provide.value('$browser', browsers[name]);
$provide.value('$document', root);
$provide.value('$sniffer', {history: name == 'html5'});
$compileProvider.directive('ngAddressBar', function() {
return function(scope, elm, attrs) {
var browser = browsers[attrs.browser],
input = angular.element('<input type="text">').val(browser.url()),
delay;
input.bind('keypress keyup keydown', function() {
if (!delay) {
delay = setTimeout(fireUrlChange, 250);
}
});
browser.url = function(url) {
return input.val(url);
};
elm.append('Address: ').append(input);
function fireUrlChange() {
delay = null;
browser.urlChange(input.val());
}
};
});
}]);
root.bind('click', function(e) {
e.stopPropagation();
});
}
initEnv('html5');
initEnv('hashbang');Demo
注意
页面的重新加载
$location服务职能让你改变URL;不能让你重新加载页面。但你需要重新加载页面或者跳转到另外的页面时,请使用更低级别的API,$window.location.href。
在作用域生命周期外使用$location
$location知道应用作用域的声明周期。但URL改变时,它会更新$location,并且调用$apply,这样所有的监听它的程序都会收到。当你在$digest阶段改变URL,那么没什么问题。$location会将改变传递给浏览器,并且通知所有的监听者。但是如应用之外使用$location的话(比如,在DOM事件中或者测试中),你就要手动调用它$apply来传递改变。
$location.path() 和 “!” “/” 前缀
一个路径应该总是以斜杠开始;$location.path()写方法会在没有前缀/时自动添加。
注意,hashbang模式中的”!”前缀实际上不是$location.path()的一部分,它其实是hashPrefix。
使用$location服务测试
当你在测试中使用$location服务时,你是处在作用域生命周期之外的,所以你要手动调用scope.$apply().
describe('serviceUnderTest', function() {
beforeEach(module(function($provide) {
$provide.factory('serviceUnderTest', function($location){
// whatever it does...
});
});
it('should...', inject(function($location, $rootScope, serviceUnderTest) {
$location.path('/new/path');
$rootScope.$apply();
// test whatever the service should do...
}));
});和之前的AngularJS版本整合
在之前版本中,$location使用hashPath或者hashSearch来处理path和搜索。在这些版本中,$location服务处理path和搜索方法,然后在需要时用它收集到的信息将hashbang URL(如http://server.com/#!/path?search=a)暴露出来。
将你的代码修改为
| Navigation inside the app | Change to |
| $location.href = value $location.hash = value $location.update(value) $location.updateHash(value) |
$location.path(path).search(search) |
| $location.hashPath = path | $location.path(path) |
| $location.hashSearch = search | $location.search(search) |
| Navigation outside the app | Use lower level API |
| $location.href = value $location.update(value) |
$window.location.href = value |
| $location[protocol | host | port | path | search] | $window.location[protocol | host | port | path | search] |
| Read access | Change to |
| $location.hashPath | $location.path() |
| $location.hashSearch | $location.search() |
| $location.href $location.protocol $location.host $location.port $location.hash |
$location.absUrl() $location.protocol() $location.host() $location.port() $location.path() + $location.search() |
| $location.path $location.search |
$window.location.path $window.location.search |
$location的双向绑定
AngularJS的编译器目前不支持对$location对象的双向绑定(参看问题列表)。如果你需要对$location对象(在input元素上使用ngModel指令)进行双向绑定,你需要指定一个带有两个监听者的额外的模型属性(比如locationPath),这两个监听者各负责一个方向。
<!-- html -->
<input type="text" ng-model="locationPath" />
// js - controller
$scope.$watch('locationPath', function(path) {
$location.path(path);
});
$scope.$watch('$location.path()', function(path) {
scope.locationPath = path;
});相关API
$location API
0 条评论。